Managing Autoimmune Disorders with Camel Milk: Insights from Recent Studies
Autoimmune disorders arise when the immune system mistakenly targets the body’s own tissues, leading to chronic inflammation, tissue damage, and a wide range of clinical symptoms. Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and inflammatory bowel disease are just a few examples where immune dysregulation plays a central role. In the search for natural and complementary therapies, camel milk has emerged as a promising candidate. With its unique nutritional profile and bioactive compounds, camel milk offers potential benefits for modulating immune responses and reducing inflammation in autoimmune conditions.
This comprehensive article reviews current scientific insights into how camel milk may assist in managing autoimmune disorders. We discuss its key bioactive components, the underlying mechanisms of action, and the latest research findings from in vitro studies, animal models, and preliminary clinical trials. By integrating these perspectives, we aim to provide a balanced, evidence-based view on the potential role of camel milk as an adjunct therapy for autoimmune disorders.
Understanding Autoimmune Disorders
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system loses its ability to distinguish between self and non-self, leading to an attack on healthy tissues. Common autoimmune conditions include:
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Characterized by chronic joint inflammation and pain.
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): Involves the immune-mediated destruction of myelin in the central nervous system.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Includes conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, where chronic inflammation affects the digestive tract.
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): A multisystem disease with widespread inflammation affecting skin, joints, kidneys, and other organs.
Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress are common denominators in these diseases. Conventional treatments often include immunosuppressive drugs and anti-inflammatory medications, but these can come with significant side effects. As a result, there is growing interest in natural interventions that could help modulate immune responses with fewer adverse effects.
Nutritional and Bioactive Profile of Camel Milk
Camel milk has been a dietary staple in arid regions for centuries. Its unique composition sets it apart from conventional cow milk and includes:
1. Proteins and Bioactive Peptides
- Whey Proteins: Camel milk has a higher proportion of whey proteins compared to casein. These proteins are easier to digest and contain essential amino acids.
- Bioactive Peptides: During digestion, proteins break down into smaller peptides with anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties. These peptides can modulate cytokine production and reduce immune system hyperactivity.
2. Unique Immunoglobulins
- Nanobodies: Camel milk contains unique heavy-chain antibodies (nanobodies) that are smaller and more stable than conventional antibodies. These may enhance immune regulation and contribute to a more balanced immune response.
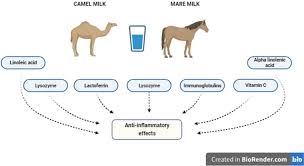
3. Lactoferrin
- Iron-Binding Glycoprotein: Lactoferrin plays a crucial role in modulating immune responses. It can inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, reduce oxidative stress, and possess antimicrobial properties—all of which are beneficial in autoimmune conditions.
4. Vitamins, Minerals, and Antioxidants
- Vitamins: High levels of vitamin C and B-complex vitamins support overall immune function and help neutralize free radicals.
- Minerals: Essential minerals like calcium, magnesium, and selenium are critical for maintaining cellular health and reducing inflammation.
- Antioxidants: The potent antioxidant capacity of camel milk helps combat oxidative stress, which is implicated in the progression of autoimmune diseases.
Mechanisms of Action in Autoimmune ModulationA. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Chronic inflammation is a key feature of autoimmune disorders. Camel milk’s bioactive compounds, particularly lactoferrin and specific peptides, have been shown to:
- Downregulate Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines: Studies have demonstrated that lactoferrin can reduce levels of cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, which are often elevated in autoimmune conditions.
- Inhibit Inflammatory Enzymes: Some bioactive peptides may inhibit enzymes like cyclooxygenase (COX), thus lowering the synthesis of inflammatory mediators.
B. Immune System Modulation
Camel milk appears to modulate immune responses rather than suppress them entirely. This balanced modulation is crucial for individuals with autoimmune disorders:
- Regulation of T-Cells: Some studies indicate that camel milk can influence T-cell activity, helping to shift the immune response from a pro-inflammatory to a more regulated state.
- Enhanced Natural Killer (NK) Cell Activity: By boosting NK cell function, camel milk may improve the body’s ability to eliminate aberrant cells without triggering widespread immune suppression.
C. Reduction of Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress, resulting from an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants, contributes significantly to tissue damage in autoimmune diseases:
- Antioxidant Properties: The high concentration of vitamin C and other antioxidants in camel milk helps neutralize free radicals, protecting cells from oxidative damage and potentially slowing disease progression.
- Protection of Cellular Integrity: By reducing oxidative stress, camel milk supports the integrity of cell membranes and other vital structures, which is crucial in mitigating inflammatory damage.
D. Gut Health and the Immune Axis
The gut microbiota plays a central role in immune regulation. Camel milk may contribute to a healthier gut environment by:
- Enhancing Probiotic Growth: The bioactive compounds in camel milk can support the growth of beneficial bacteria, which in turn modulate immune responses.
- Improving Gut Barrier Function: A robust gut barrier prevents the translocation of harmful substances that can trigger systemic inflammation.
Scientific Evidence from Recent StudiesIn Vitro Research
Laboratory studies provide a foundational understanding of camel milk’s potential benefits:
- Cell Culture Studies: Experiments using human immune cells have demonstrated that camel milk extracts can reduce the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and inhibit markers associated with immune overactivation.
- Antioxidant Assays: In vitro assays reveal that camel milk exhibits high antioxidant activity, which may protect cells from oxidative damage linked to autoimmune processes.
Animal Studies
Animal models offer insight into the potential therapeutic effects of camel milk:
- Rodent Models of Autoimmunity: Studies in rodents have shown that dietary supplementation with camel milk can lead to reduced inflammatory markers, improved oxidative stress profiles, and modulation of immune cell populations.
- Disease-Specific Models: In experimental models of rheumatoid arthritis and colitis, camel milk supplementation was associated with decreased joint inflammation and improved intestinal health, respectively. These findings suggest that camel milk may attenuate disease severity through its anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects.
Human Clinical Trials
Preliminary clinical studies in humans have started to explore the role of camel milk in managing autoimmune disorders:
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Early clinical trials in patients with rheumatoid arthritis have reported improvements in joint pain, reduced inflammation, and enhanced mobility after regular consumption of camel milk.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Patients with IBD who incorporated camel milk into their diets experienced a reduction in gastrointestinal symptoms and markers of systemic inflammation.
- Multiple Sclerosis: Although research is still in the exploratory phase, some pilot studies suggest that camel milk may help improve quality of life and reduce fatigue in patients with multiple sclerosis.
While these clinical studies are promising, larger, long-term randomized controlled trials are needed to confirm and expand upon these findings.
Practical Considerations and Dietary IntegrationHow to Incorporate Camel Milk
Integrating camel milk into the diet can be a straightforward process:
- As a Beverage: Drinking fresh or pasteurized camel milk is the simplest way to enjoy its benefits.
- In Culinary Applications: Camel milk can replace cow milk in smoothies, cereals, and recipes for baked goods, offering versatility in everyday meals.
- Powdered Form: In regions where fresh camel milk is not available, powdered camel milk provides a convenient alternative that retains much of its nutritional and bioactive integrity.
Dosage Recommendations
Although research on the optimal dosage is ongoing, many studies have utilized daily intakes ranging from 250 to 500 milliliters. It is recommended to start with a moderate amount and gradually increase consumption while monitoring for any adverse effects. As always, individuals with specific health conditions should consult a healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes.
Complementary Lifestyle Practices
For optimal management of autoimmune disorders, camel milk should be part of a comprehensive approach that includes:
- A Balanced Diet: Rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to support overall immune health.
- Regular Physical Activity: Exercise helps reduce inflammation and improves immune function.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, or mindfulness can help modulate immune responses and reduce flare-ups.
- Adequate Hydration and Sleep: Both are essential for maintaining immune system balance and overall health.
Future Directions and Research Needs
Despite promising preliminary findings, further research is necessary to fully elucidate the role of camel milk in managing autoimmune disorders:
- Long-Term Clinical Trials: Larger, randomized controlled trials will help establish the long-term efficacy and safety of camel milk in autoimmune conditions.
- Mechanistic Studies: Further investigations into the molecular pathways modulated by camel milk’s bioactive compounds will provide deeper insights into its therapeutic potential.
- Standardization of Camel Milk Products: Variations in camel milk composition due to factors such as breed, diet, and processing methods need to be standardized to ensure consistent clinical outcomes.
- Synergistic Effects: Research on the combined effects of camel milk with conventional therapies may help optimize treatment protocols for autoimmune disorders.
Conclusion
Camel milk shows significant promise as a natural, complementary intervention for managing autoimmune disorders. Its unique blend of bioactive compounds—ranging from immunoglobulins and lactoferrin to bioactive peptides and potent antioxidants—appears to modulate immune responses, reduce chronic inflammation, and mitigate oxidative stress. These mechanisms are crucial for alleviating the symptoms of autoimmune diseases and improving overall quality of life.
While further large-scale clinical research is needed to confirm these benefits, the current body of evidence supports the potential role of camel milk as a valuable component of a comprehensive autoimmune management strategy. Incorporating camel milk into a balanced diet, along with other healthy lifestyle practices, may offer a natural way to help control autoimmune responses and promote long-term wellness.
For those interested in experiencing the remarkable benefits of camel milk firsthand, the finest quality camel milk in Germany and Europe can be obtained from Camel Way Europe company. Explore their offerings and discover premium products such as the 3 Packs of Camel Milk Powder 300g (total 900g). Discounted Bulk Pack!, visit CamelWay Camel Milk, and learn more about the Camel Milk Benefits.




